
Fundamenteel Onderzoek
Antwerp diamond research
Aim
The activities of the research department are crucial in supporting HRD Antwerp’s main activity, i.e. the issuing of diamond
certificates by Diamond Lab. The determination of the 4 Cs requires state-of the-art equipment and techniques which are in general
not commercially available. HRD Antwerp Research defines the necessary developments to secure and enhance the 5th C (Confidence)
on the diamond certificate and collaborates closely with diamond research institutes and centers, in particular with WTOCD.
The general aims of HRD Antwerp Research are:
• To develop non-destructive methods for the identification of treated and synthetic diamonds
• To implement the methods of identification and detection in the process of HRD Antwerp Diamond Lab
• To inform the diamond community on scientific and technological developments related to gem diamond
• To provide a Scientific Advice Service to support the diamond community
Research topics
Synthetic diamond
At present, two methods exist to produce large synthetic diamonds of gem quality: High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD).In the HPHT process, natural diamond growth parameters are imitated. The HPHT method dates from the 1950s. Large gem quality stones are known since the 1970s.
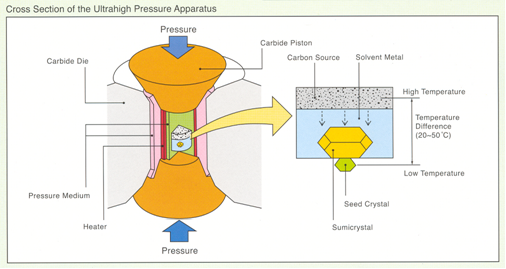
Schematic setup of a “Belt” apparatus for the production of HPHT synthetic diamonds
(Sumitomo).
(Sumitomo).

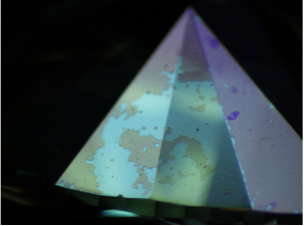
Rough HPHT synthetic diamond
CVD diamond is created from the gas phase, by deposition of carbon from a plasma; the CVD method for producing synthetic diamond has existed for more than half a century, but gem quality stones are still very rare commercially.
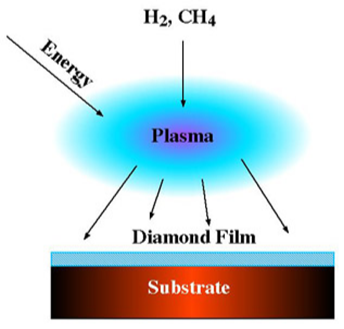

Schematic setup of a system for the production of
CVD synthetic diamond.
CVD synthetic diamond.
Polished CVD synthetic diamond
Treatments
The purpose of a treatment is to enhance one or more of the four Cs of a diamond, increasing the value of the stone. Especially clarity and colour treatments are important and they are known since a long time. In fact diamonds have been treated long before man was capable of making synthetic diamonds. Both natural and synthetic diamonds can be treated.Colour treatments
| Treatment | Result | How? | Example |
| Irradiation | Create blue to green (fancy) colours | High energy irradiation (e.g. 1 MeV electrons) |
  Blue-green irradiated diamond |
| Irradiation + heating | Create yellow, orange, pink and even red fancy colours | High energy irradiation + heating up to 1000°C |
  Yellow diamond, type Ia, irradiated and heat treated |
| Coating | Create all fancy colours Blue coating makes a yellowish stone more colourless Easily damaged |
Surface layer of coloured foreign material Synthetic CVD diamond layer is possible |
  Damaged coating on a polished diamond |
| HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) treatment | Make a stone more colourless (type IIa or IaB), or create fancy colours | High temperature (>2000°C) High pressure (>70000 atm) |
  Blue diamond, type IIb, HPHT treated |
| HPHT + irradiation + heating | Create pink to red colours | HPHT + High energy irrradiation + heating up to 1000°C |
  Pink diamond, type Ia, HPHT treated, irradiated and heated |
| High temperature treatment | Create black colour | Heating to around 1000°C (oxygen free atmosphere) Boart quality diamond |
  Black diamond, heat treated |
Clarity treatments
| Treatment | Result | How? | Example |
| Laser drilling + deep boiling | Improved clarity because of reduced visibility of inclusion(s) | Laser hole drilled from inclusion to surface + inclusion bleached chemically |
 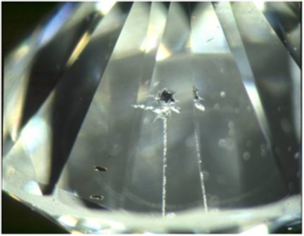 Laser drilling in a polished diamond |
| Fracture filling | Improved clarity because of reduced visibility of fractures | High refractive index glass introduced in the fractures |
 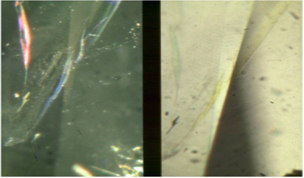 “Flash effect” colours in a fracture filled diamond |
Scientific Advice
HRD Research offers a scientific advice service to the diamond sector. Supported by a wide range of analysis instruments, practical solutions are offered to challenges of a scientific nature. These challenges can relate to the necessity of identifying synthetic and treated diamonds, the evaluation of rough stones, the identification of different types of diamonds, etc. The aim is to provide support to diamond the sector, and to enhance consumer confidence.Contact information
HRD Antwerp – ResearchHoveniersstraat 22
B-2018 Antwerpen
Belgium
Tel: +32 3 222 06 11
Fax: +32 3 222 06 99
E-mail:
Website: www.hrdantwerp.be